Financial Module cash receipt ( Incoming )
By cash receipts , we can record incoming cash
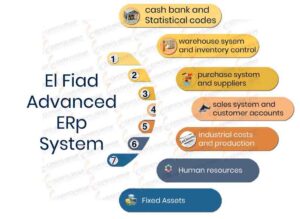
Financial Module
- Cash receipt ( Incoming )
By cash receipts , we can record incoming cash from outside the company such as customers payments or internal bodies such as proceeds of salesmen , Covenant settlements or transfers from banks … etc. - Cash receipt (Issued)
Payment of any obligations on a company such as suppliers, payment of expenses, salaries, bank transfer…etc. - Check ( issued )
The payment of any obligation on the company to any entity through the bank indicating the date of issue of the check, the date of maturity of the check and the bank issued by it and the person or company to be repaid - Check ( Incoming)
recording any debts from any person such as customers through bank checks explaining the date of collection of the check and client’s bank - Bank Notice
Proof of any deposits in the company’s bank accounts , such as deposit of customers or transfers from abroad, transfers from the treasury to the bank, financing of the bank account through the partners’ neighbors, bank returns, …etc. - Bank Debit Notice
Proof of any withdrawals made on the company’s bank account or transfers to pay a liability to the company, such as repayments of overseas suppliers in case of import, as well as the opening of the documentary credit or debits by the bank such as payment of bank expenses or interest, etc - Letter of guarantee
There are two types of letters of guarantee, letters of guarantee issued, and letters of guarantee contained, used in the case of tender entry or otherwise - Revenue Invoice
In the case of companies that provide certain services to their customers, such as transport companies or customs clearance companies, indicating the services, price of each service, and the various types of tax, such as sales tax, discount tax, addition…etc. - Expense Invoice
When requesting a specific service from some companies that provide services, such as transporting goods to the port, customs clearance service or tax services, a service invoice is recorded showing the price of each service separately and sales taxes - Statistical items
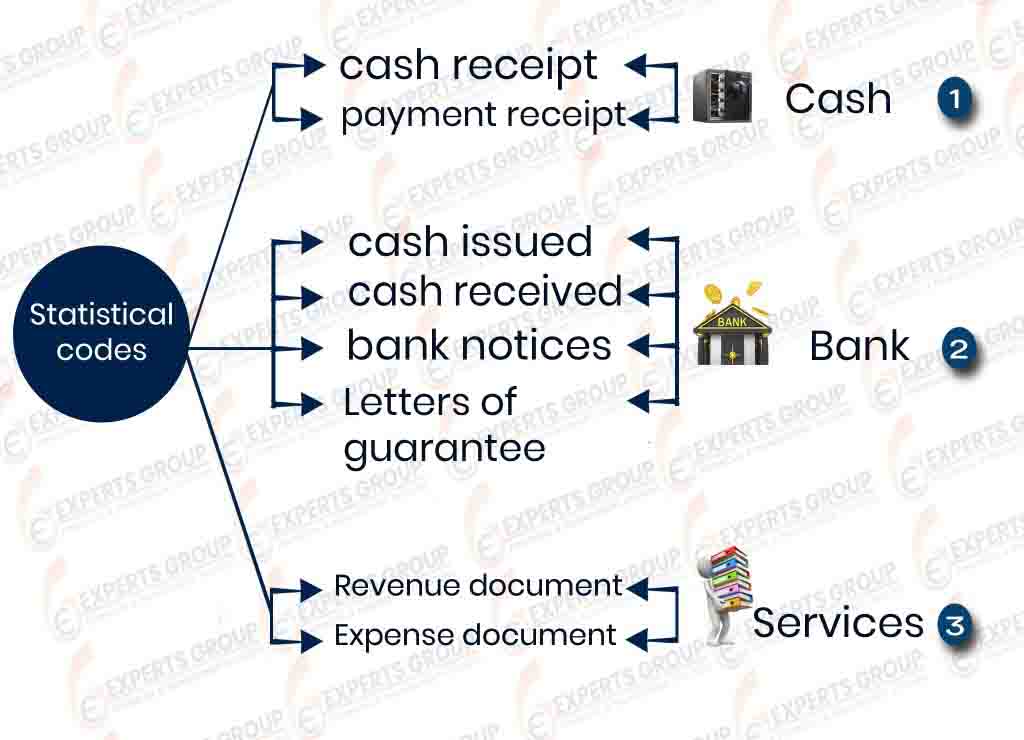
Where some accounts can be analyzed without analysis in the accounts tree, which leads to the large number of accounts and levels in the accounts tree , where it requires a great effort in the search and recording financial transactions, through using statistical items you can analyze some accounts or expenses like selling expenses ,car expenses you can record the costs of each Car like fuel – maintenance – spare parts ,fixes… etc. - Financial reports
Through this module we can extract many periodic reports (daily, monthly and annual) , financial statements such as profit and loss, balance sheet, income statement, cash budget, cash flow statement - Designing reports
sometimes top management needs reports with a specific shape, by Report Designer,
you can create any financial report with any columns and aggregations.
Purchasing Module
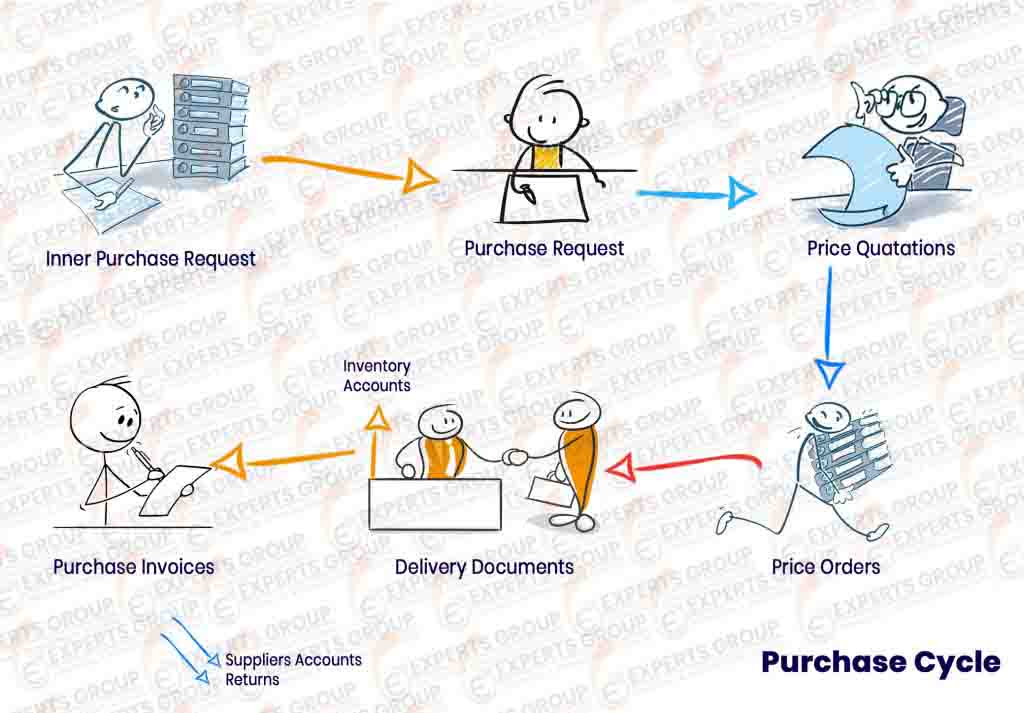
Purchasing cycle
- Purchase request ( PR )
The requests submitted by the warehouses to the purchasing department through which the needs of each warehouse are determined to fill the shortage with the identification of the required items showing the quantities of each item, the procurement department sorts the orders and is submitted to the senior management for approval and take the necessary measures to implement them
- Gathering purchase requests
purchasing department collect all requests from all warehouses in one request
containing all items, and dividing this request to many POs .
- Quotations
Record all the quotations provided by the suppliers, specifying the supplier and the items that can be supplied to the company, Delivery period, any taxes and expenses.
- Purchase Order (PO)
The Purchasing Department will issue a purchase order for each supplier based on the selection of the best price and the best quality, with a time limit for the supply, to meet the needs of the Department of warehouses submitted purchase orders approved by the senior management
- Purchase Invoice
The supplier sends the purchase invoice to the company at the prices agreed upon by the purchase order, stating how the payment is made, cash or forward, all deductions and taxes, such as sales tax or discount tax , After the invoice is registered, an accounting entry is generated automatically and the various account balances are changed.
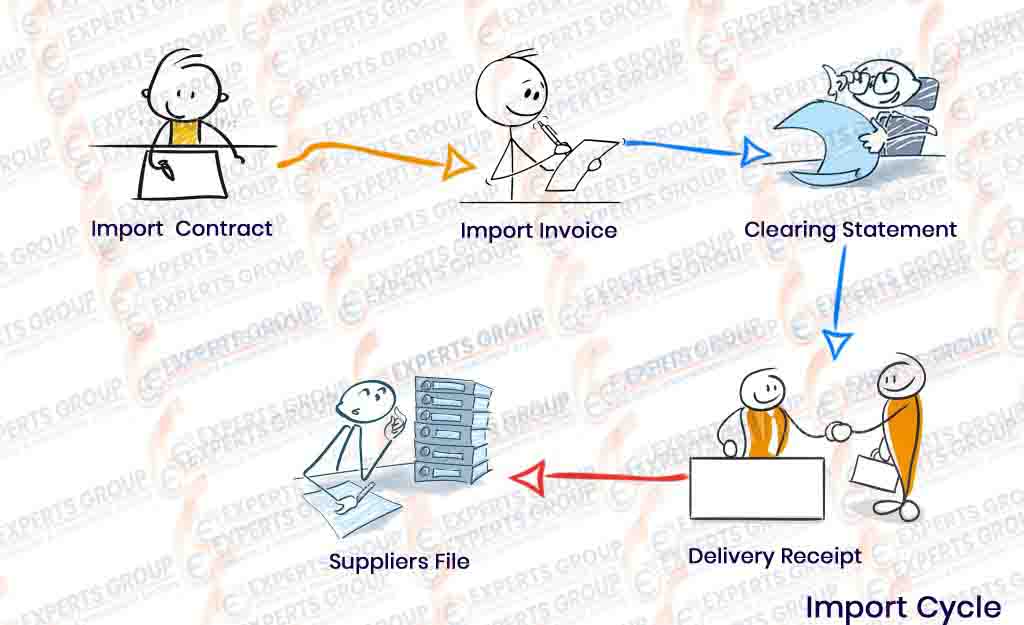
Importing cycle
- Import Contract
Sometimes when the company imports items from the external supplier, the purchasing department in agreement with the external supplier to supply the items at a specified purchase price and supply within a certain period of time, with an agreement on the terms of payment, and this is done through an import contract to ensure the seriousness of the deal, and the company is not exposed to risks Lack of raw materials for manufacturing during the year - Import Invoice
The supplier sends the import invoice to the company in accordance with the contract concluded with the company, showing the quantity and value of the goods received, after opening a documentary credit through the bank, and the invoice shows the shipping expenses in foreign currency and any other expenses, and shipping expenses can be distributed on items in several ways such as cost or weight or size - Clearing Statement
Company is in agreement with the clearance offices to receive the goods from the customs, and the customs broker will pay the various expenses such as tax, flooring….etc.
The Savior provides a statement to the company by the expenses that were spent on the goods until the arrival of the stores - Delivery Receipt
The warehouse department receives the goods received with a receipt. The goods are priced automatically through the system after all expenses are distributed at their exchange rate
Sales Module
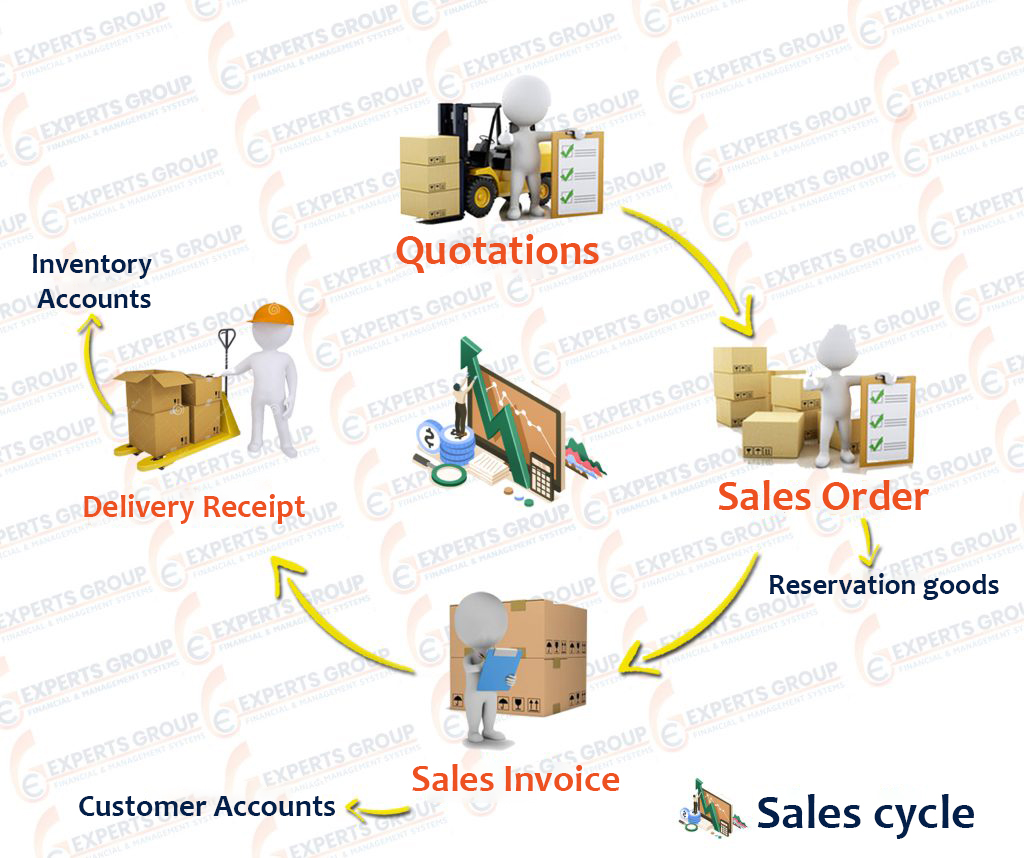
Sales cycle
- Quotations
When customers request clarification of the prices of some items sold by the company, the company makes quotations to customers showing the prices of items and the period of supply and terms of payment and any deductions or taxes paid by the customer
- Sales Order ( SO )
After approval of the prices submitted by sending a sale order to the company in the required goods according to the prices agreed through the offers submitted or through the sales price lists of the company - Sales Invoice
The sales department issues a sales invoice at the prices agreed upon in the sale order, stating all deductions and taxes, whether sales tax or deduction tax. The system generates an accounting entry and directly influences customer and other accounts - Delivery Receipt
The warehouse department will deliver the goods based on the sales order through the delivery of goods only - Reservation goods
The company makes a reservation of goods in the items in the sale order and does not exist in the stores, or the goods that are in the stores and the customer does not want to receive them at the moment, and thus ensures not to dispose of them - Sales Planning
The sales department makes a sales plan during the year with the items to be sold taking into account the periods of stagnation and popularity, the system determines the type of plan (targeted – confirmed – implemented) where the year is divided into 52 weeks
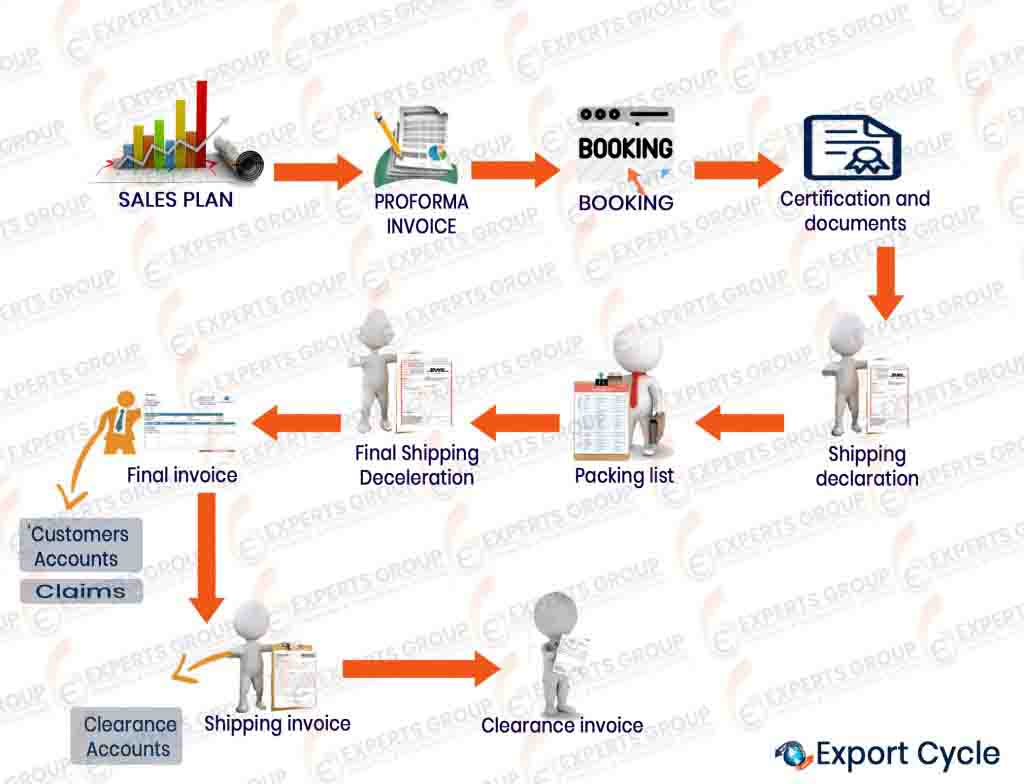
Export Cycle
After preparing the final product the export department starts to execute all procedures to export the final product starting with :-
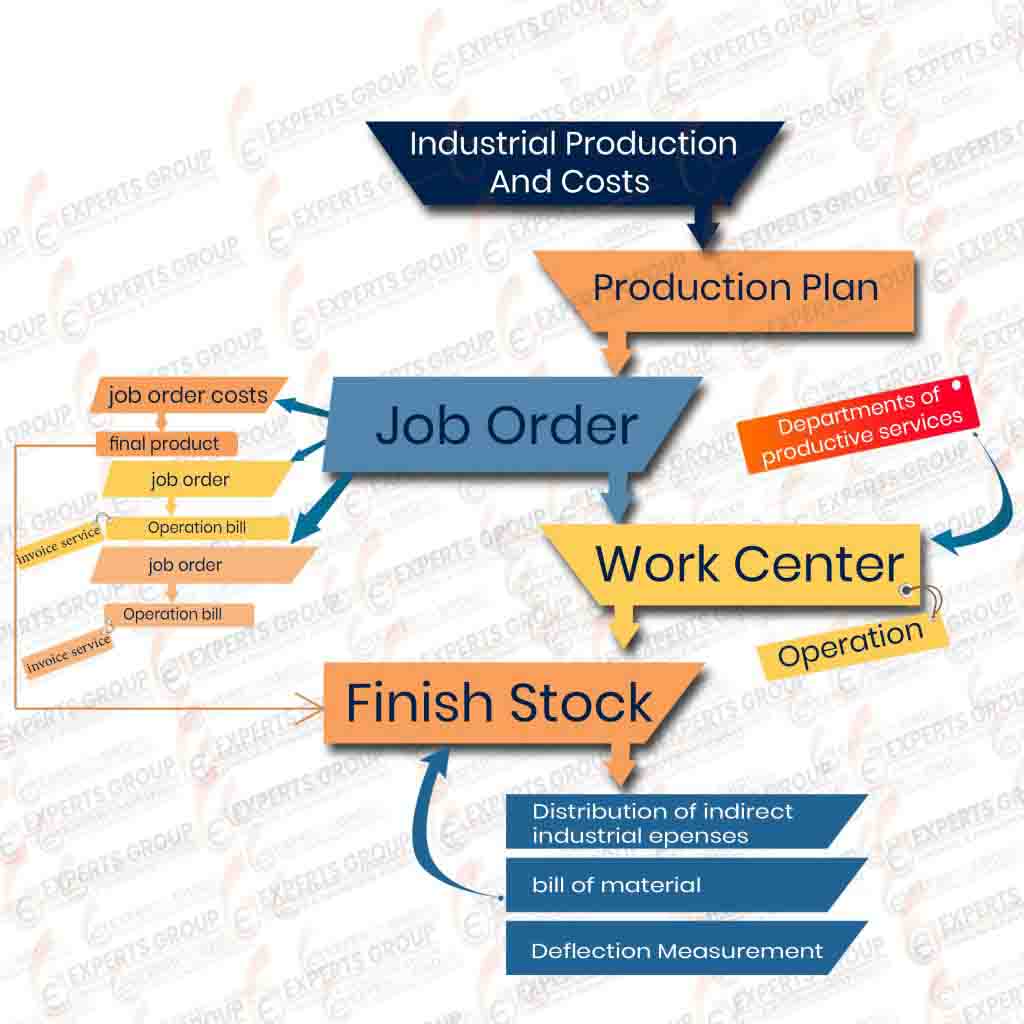
Costing & Production Module
- Production Plan
is based on the annual sales plan and through the plan provide the necessary resources of raw materials and supplies, as well as provide the necessary labor during the production season, whether permanent or temporary labor
- Job Orders
Through the system, work orders can be divided into:
- Production orders :- related to the company’s production
- Orders for third parties :- where the company performs manufacturing
processes for others - Orders with third parties :- The company operates at third parties factories , through
which it is possible to know the costs of each order separately
and its share of materials, wages and indirect industrial costs. - Work Centers
These are the sections where operations are carried out, such as welding and installation or packaging , the area of each section and the bases for the distribution of fixed and variable industrial expenses are determined, with the operational processes of the department
- Work Operations Following
Control within the operating halls is carried out by the Labor sheet to determine the operating hours of each labor on the order and the operational process carried out by him and to identify faults time, this is useful :- - determining the cost of the matter accurately and shows how efficient labor,
- The operating hours of the machines are determined to accurately distribute the cost of the motors through the process supervisors
- Service Centers
They are sections that serve the operational process but indirectly, such as factory maintenance department, warehouse department and accounts department, and these sections consist of indirect costs are redistributed again to the production departments, and the cost accrued in the service departments is redistributed to the production departments in any of the ways Recognized distribution (reciprocal – descending – solitary – total), according to the proportions of distribution, which is appropriate for each industry, or as perceived by the cost accountant - Expenses Distributions
Elements of indirect industrial costs, both fixed and variable, are charged to the productive or service departments, either directly, or the element is considered a general cost and is distributed to a group of departments according to the proportions of distribution that the cost accountant sees and is done through the distribution of expenses. - Standard mensuration
An assay is made for each product separately and shows the raw materials and supplies for the production of the product unit and operating hours for each operation individually and this is useful in monitoring performance and determine the aspects of deviation and thus provisions for control of operation and measure the efficiency of the labor. - Final Product Pricing
The loading rates (fixed – variable) are extracted for each production section, where the fixed load rate is calculated on the basis of maximum operating hours, the variable load rate is based on actual operating hours, and the load rates can be calculated on other bases.
The cost of the production divisions is distributed among the production orders according to the operating hours that the order has benefited within the department.
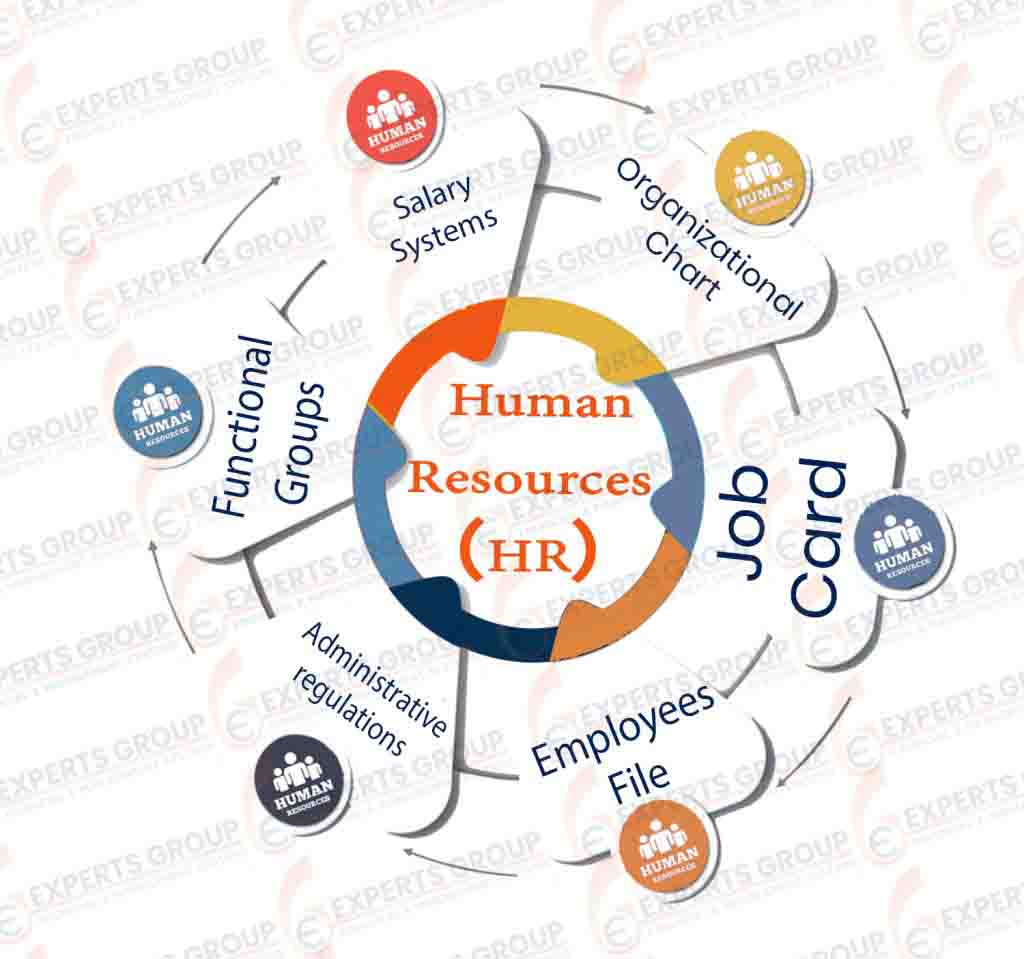
Human Resources (HR)
- Organizational Chart
It represents the schematic form of the various departments of the company (main – sub – sections) within the company, which is a tree structure that starts from the top management and ends with the lower departments and sections - Job Card
It represents the schematic form (financial manager – accounts manager – accountant …… etc.) with the job grades for each card and the experience of each employee, and the degree of qualification required by the job with a statement of the objective. - Employees File
– Specific recruitment data for each employee (date of appointment – department or department –
social insurance – branch – rosary – wage system …… etc.).
– Labor’s personal data (gender, marital status, card number, educational qualification, etc.).
– Vocabulary of salary (salary basis – allowances) obtained by the labor or employee.
- Administrative regulations
Which can be configured to suit the system and working conditions of any company and include: –
• List of delays.
• List of overtime.
• List of official holidays.
• List of commissions.
• Sanctions Regulation.
It can calculate the extra hours, commissions and the value of working hours during official holidays.
–Also calculate the value of deductions represented in the value of the delay by linking with the record of attendance and leave, and other deductions such as social insurance and advances and the value of any other sanctions
- Functional Groups
You can classify employees into groups ,each group has some common characteristics such as Wages system, daily working hours and regulations, morning and evening shifts.
- Salary Systems
There are several salary systems such as :-
- Monthly system
- Duration of remuneration system (daily, weekly, unequal periods)